Enable Cloner Modifier
- Select the object you want to clone
- Find the Modifiers Panel on the properties sidebar
- Press the ”+” button and choose Cloner
Cloner and Randomness parameters can be animated via state change to achieve procedural motion
Cloning Types
The following types are available in Cloner: Radial, Linear, Grid, and Object. Each type allows the generation of a different pattern. Each type can be randomized by turning on the Randomness.Radial
Radial type is a perfect start to create clones along a circle.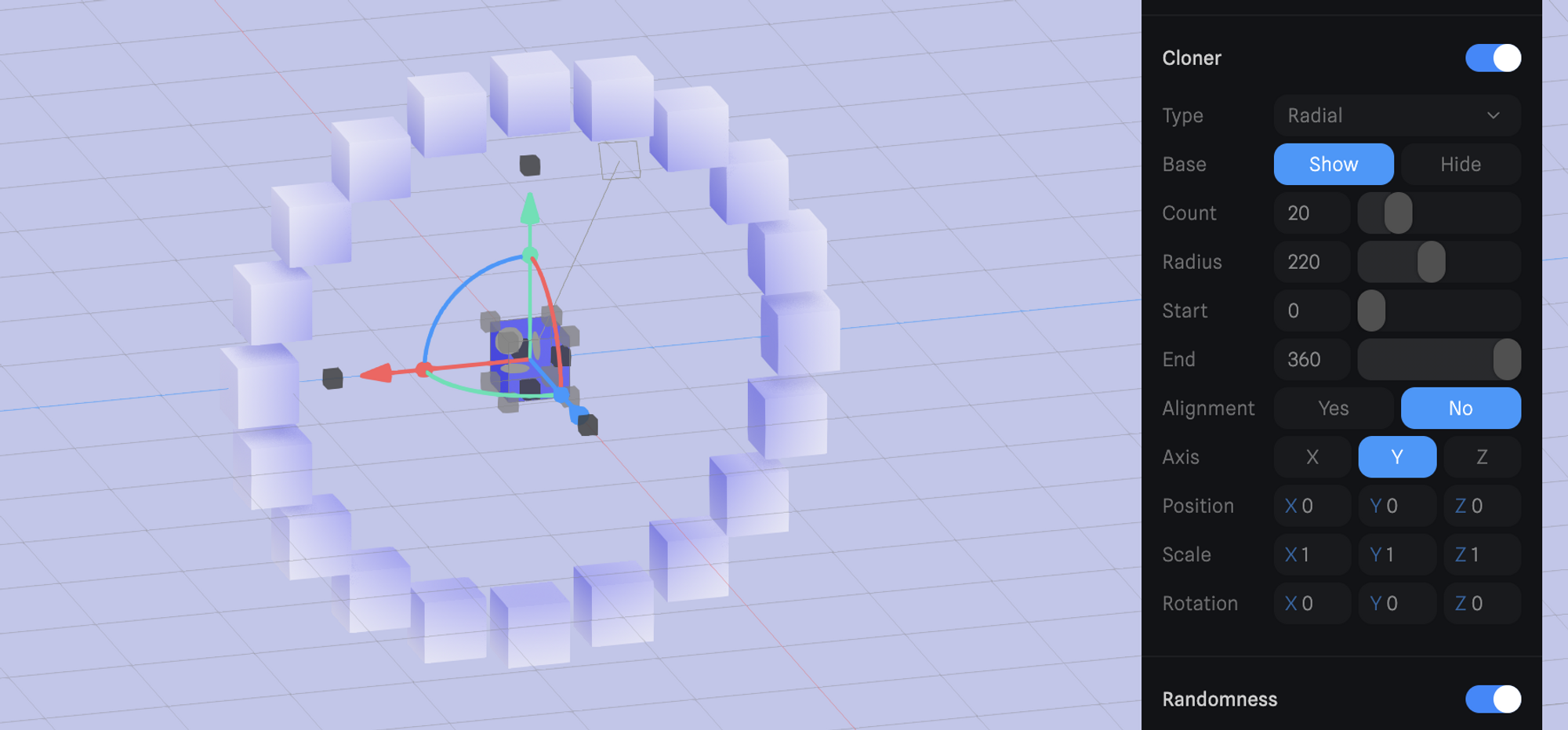
- Base → Ability to show or hide the original cloned object.
- Count → Amount of clones to be created.
- Radius → Size of the radius.
- Start/End → Allows to define a circular sector, it’s set to a full circle by default.
- Alignment → Aligns the clones to the radius if active.
- Axis → set the orientation of the Radial Clones based on X/Y/Z
- Transform (Position, Scale, Rotation) → Modify the transform values of the clones (the base object will keep the original transform).
Linear
Linear type is a simple clone in one direction based on the base object’s direction.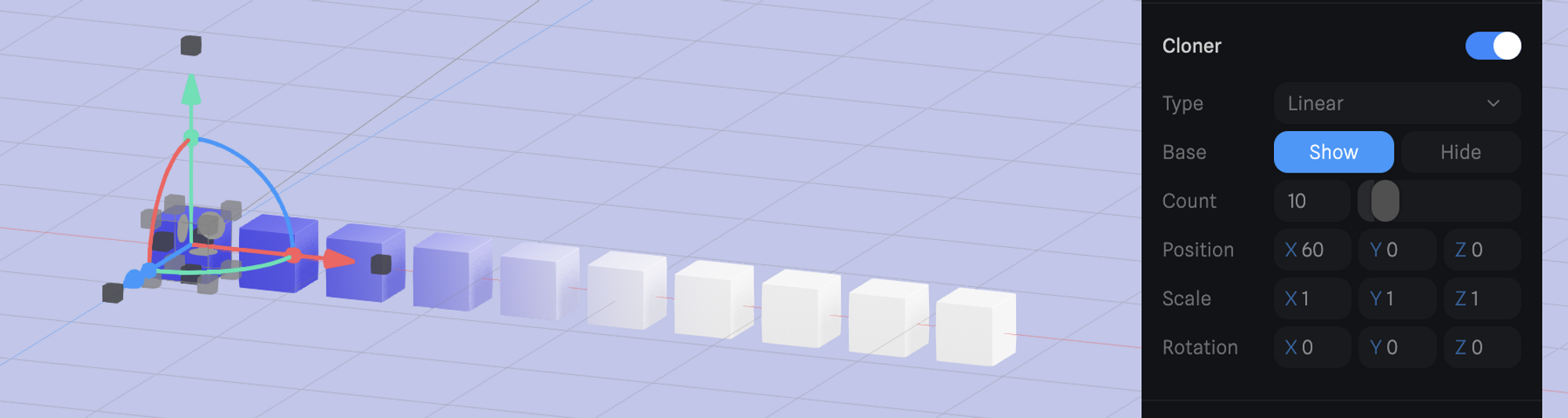
- Base → Ability to show or hide the original cloned object.
- Count → Amount of clones to be created.
- Transform (Position, Scale, Rotation) → Modify the transform values of the clones (the base object will keep its original values).
Grid
Grid type is able to clone objects along a 2D or 3D grid.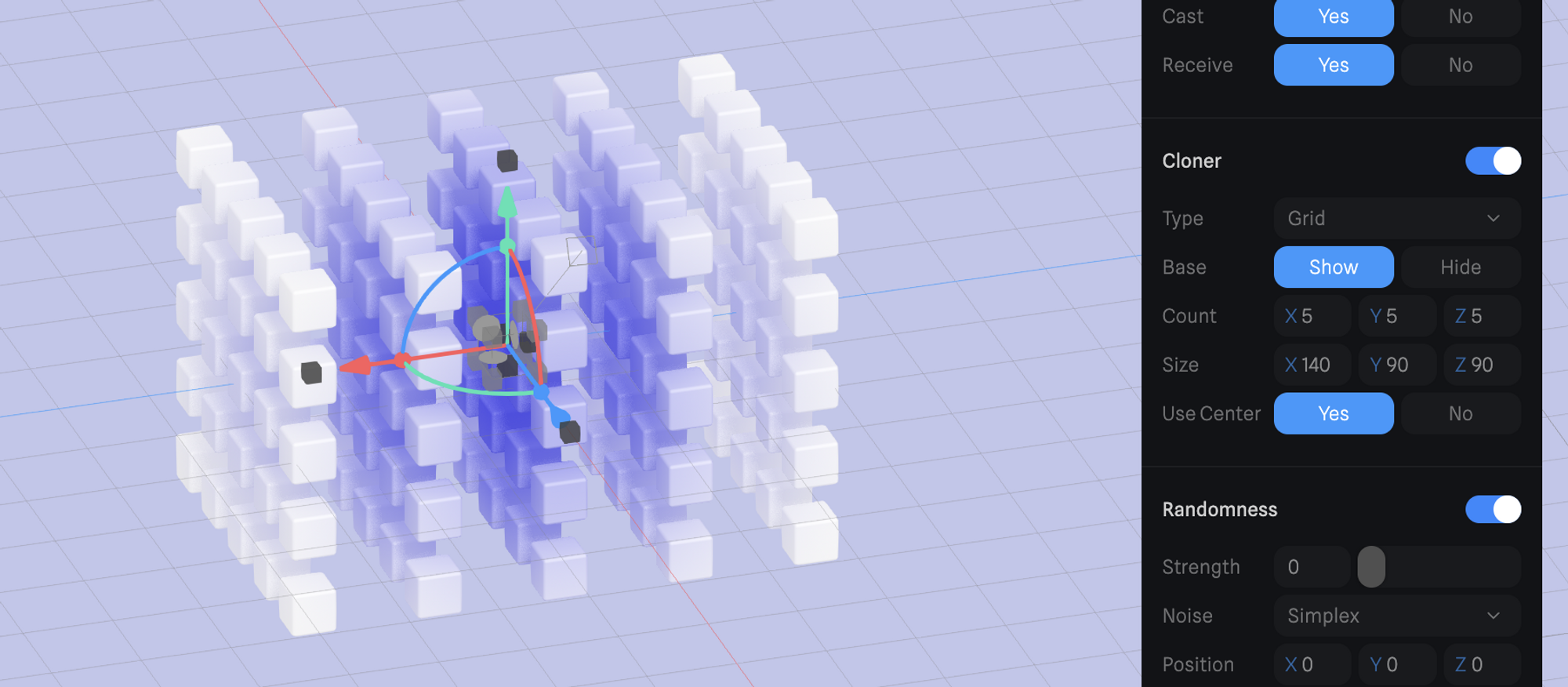
- Base → Ability to show or hide the original cloned object.
- Count → Amount of clones to be created along each axis of the grid (X, Y, Z).
- Transform (Position, Scale, Rotation) → Modify the transform values of the clones (the base object will keep its original values).
- Size → Spacing between the clones can be defined for each axis (X, Y, Z).
- Use center → Base object can be aligned to the center of the grid or it can be the initial object in the clone sequence.
Object
Object type can create more advanced results where clones can be aligned along the surface of another object.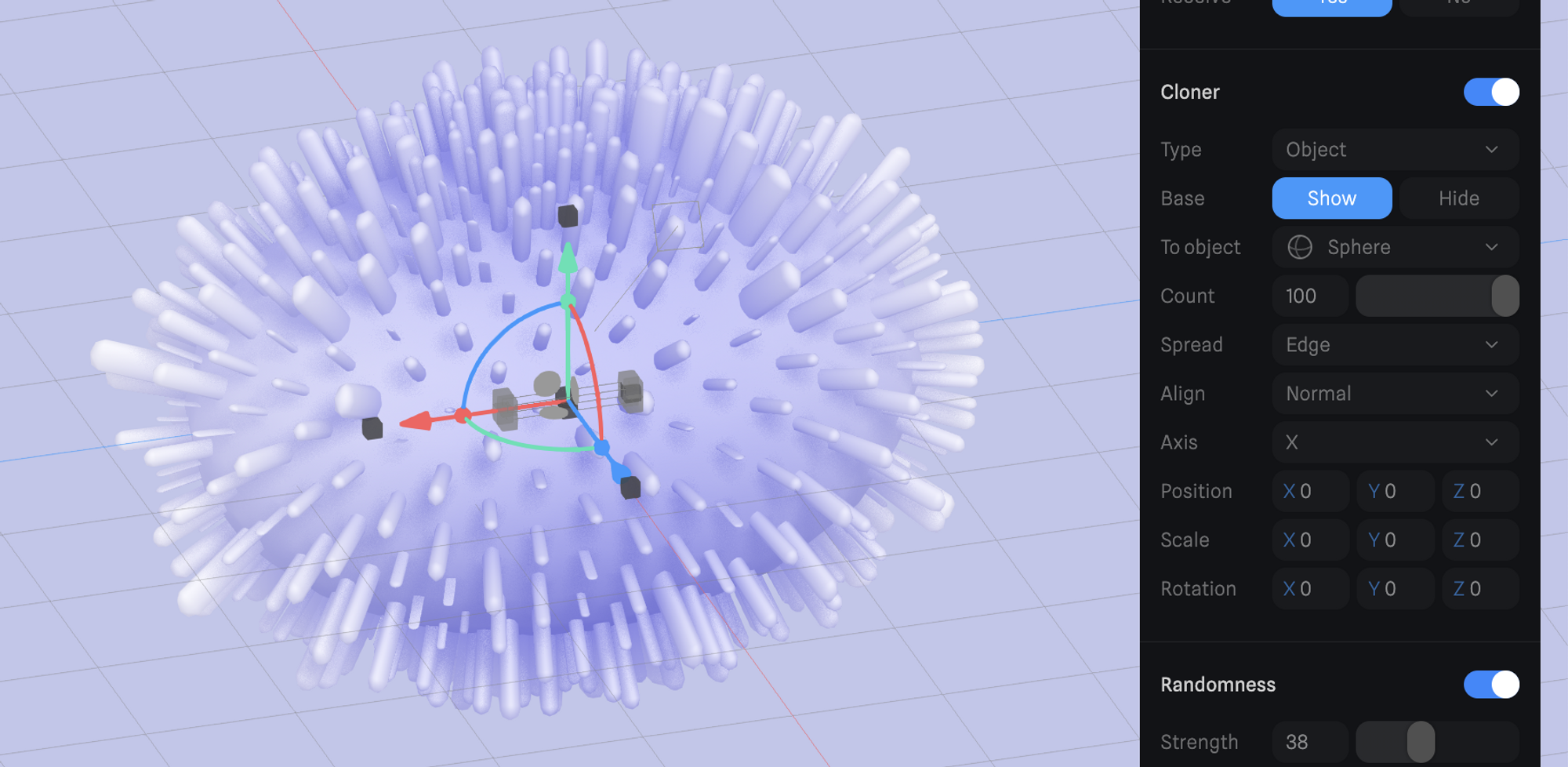
- Base → Ability to show or hide the original cloned object.
- To object → Select the reference object based on which the clones will be created.
- Count → For Random, the spread type it’s defining the number of clones to be created. For the Polygon center, Edge, and Vertex spread types, the number of clones can be defined via percentages from 0 to 100.
- Spread → Defines the distribution of the clones on the “To object”. The following types are available:
- Random → Randomly places the clones on the surface of the “To object”.
- Seed → Set an arbitrary number to generate various random patterns.
- Polygon center → Places the clones on the polygons of the “To object”.
- Edge → Places the clones on the center of the “To object” edges.
- Vertex → Places the clones on the vertices of the “To object”.
- Random → Randomly places the clones on the surface of the “To object”.
- Align → Set to “Normal” will be aligned to the “To object” normals. By setting it to “Axis” it will be based on the selected world axis.
- Axis → Preferred axis for both “Normal” and “Axis” Align types (X, X-, Y, Y-, Z, Z-)
- Transform (Position, Scale, Rotation) → Modify the transform values of the clones (the base object will keep its original values).
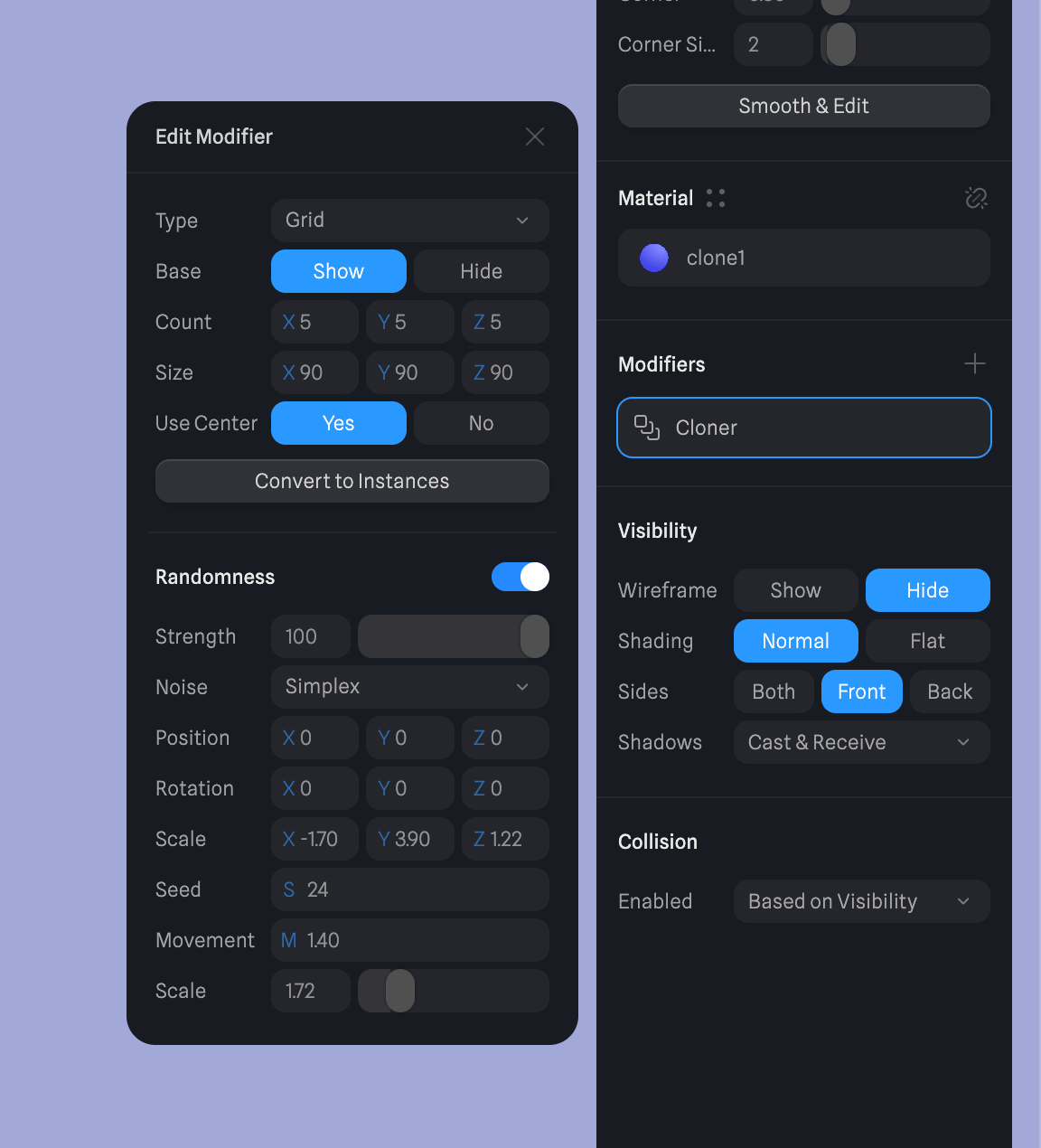
Randomness
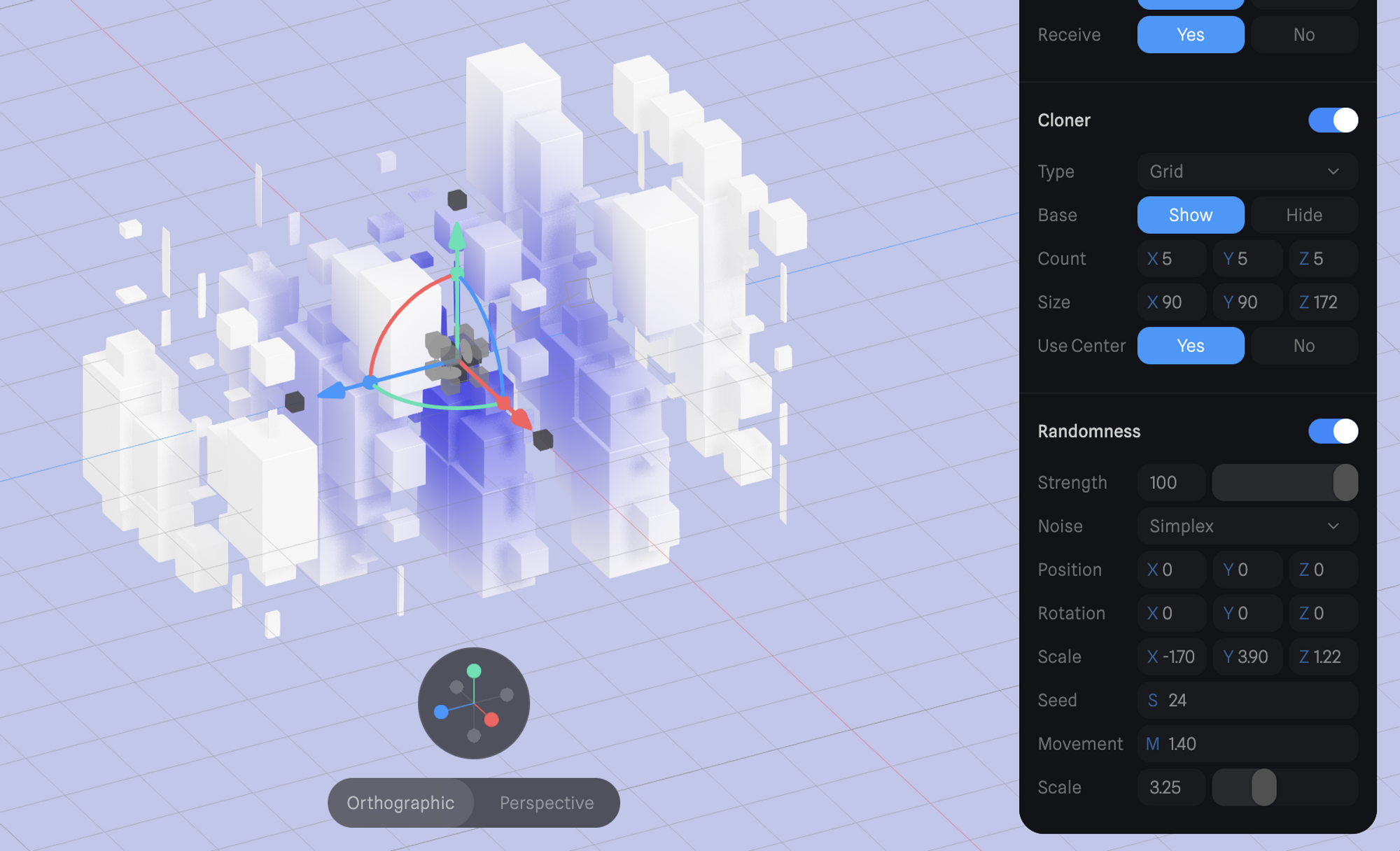 If Cloner is turned on,
If Cloner is turned on, Randomness can be applied below the Cloner to modify the cloner with random parameters. Randomness works with all Cloner types (Radial, Linear, Grid, Object).
The following parameters can be adjusted in Randomness:
- Strength → How strong the Randomness should be applied. If set to 0, randomness won’t be visible.
- Noise → Noise can be set to Perlin or Simplex. Perlin noise has higher contrast for more drastic effects.
- Transform → X, Y, and Z values can be randomized for Position, Rotation, and Scale. Try to play around with these values to achieve diverse results.
- Seed → Set an arbitrary number to generate various random patterns.
- Movement → Applies movement for the noise of the randomness which creates motion for the cloned objects.
- Scale → Adjust the value to amplify the size of the applied noise.
Pro tip: To achieve procedural motion animate these values with state-based animations.
How state-based animation works

